EPON Solutions to Electric Power Distribution Automation Systems in Smart Grid
“Smart grid”, also called “Grid 2.0”,generally refers to a class of technology people are using to bring utilityelectricity delivery systems into the 21st century, using computer-based remotecontrol and automation. These systems are made possible by two-waycommunication technology and computer processing that has been used for decadesin other industries. They are beginning to be used on electricity networks,from the power plants and wind farms all the way to the consumers ofelectricity in homes and businesses. They offer many benefits to utilities andconsumers -- mostly seen in big improvements in energy efficiency on theelectricity grid and in the energy users' homes and offices.
Situation of the Grid Communication System
Thetraditional grid communication system has greatly hindered the development ofelectric power distribution automation systems, because many techniques (suchas GPRS/CDMA, 230MHzwireless broadcasting stations, power private optical fibers, PSTN and PLC) inthe traditional grid communication system expose obvious disadvantages infunctions. For instance, the single point failure is likely to occur in thetransmission link, which impairs the capacity of service protection. Thecommunication medium and service interfaces are hard to manage and maintain, asthey are so complicated. With the narrow transmission bandwidth, the key datetransmission cannot be guaranteed and the integrated service is difficult toexpand. Besides, the internal information security in the electric power sectormay be under threat, as GPRS/CDMA is supported by the operator networkplatform.
Bycontrast, Electric Power Distribution Automation not only improves all the deficienciesin traditional grid communication system, but is more efficient. Therefore,upgrading the grid communication system is on the top of the top priority inconstructing a modern Smart Grid.
ElectricPower Distribution Automation is consisted of several systems such asSupervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA),Substation Automation (SA) and Distribution Automation (DA).
NetworkingSolution
Instead oftraditional GPRS/CDMA or 230MHz networking solution, the EPONnetworking solution has become the best choice of electric power communicationplatform. As a pioneer in this field, BDCOM introduces its own EPON solutions.These solutions involve three parts: Power management substation (such as,110KV substation), transmission channel and data collection and user-endaccess.
Here presents four BDOMEPON solutions of Electric Power Distribution Automation Systems in detail:Solution to Electric Power Distribution Automation Systems (1), Solution toElectric Power Distribution Automation Systems (2), Solution to the UserInformation Collection System, and Solution to Digital Transformer Station.
Solutionto Electric Power Distribution Automation Systems (1)
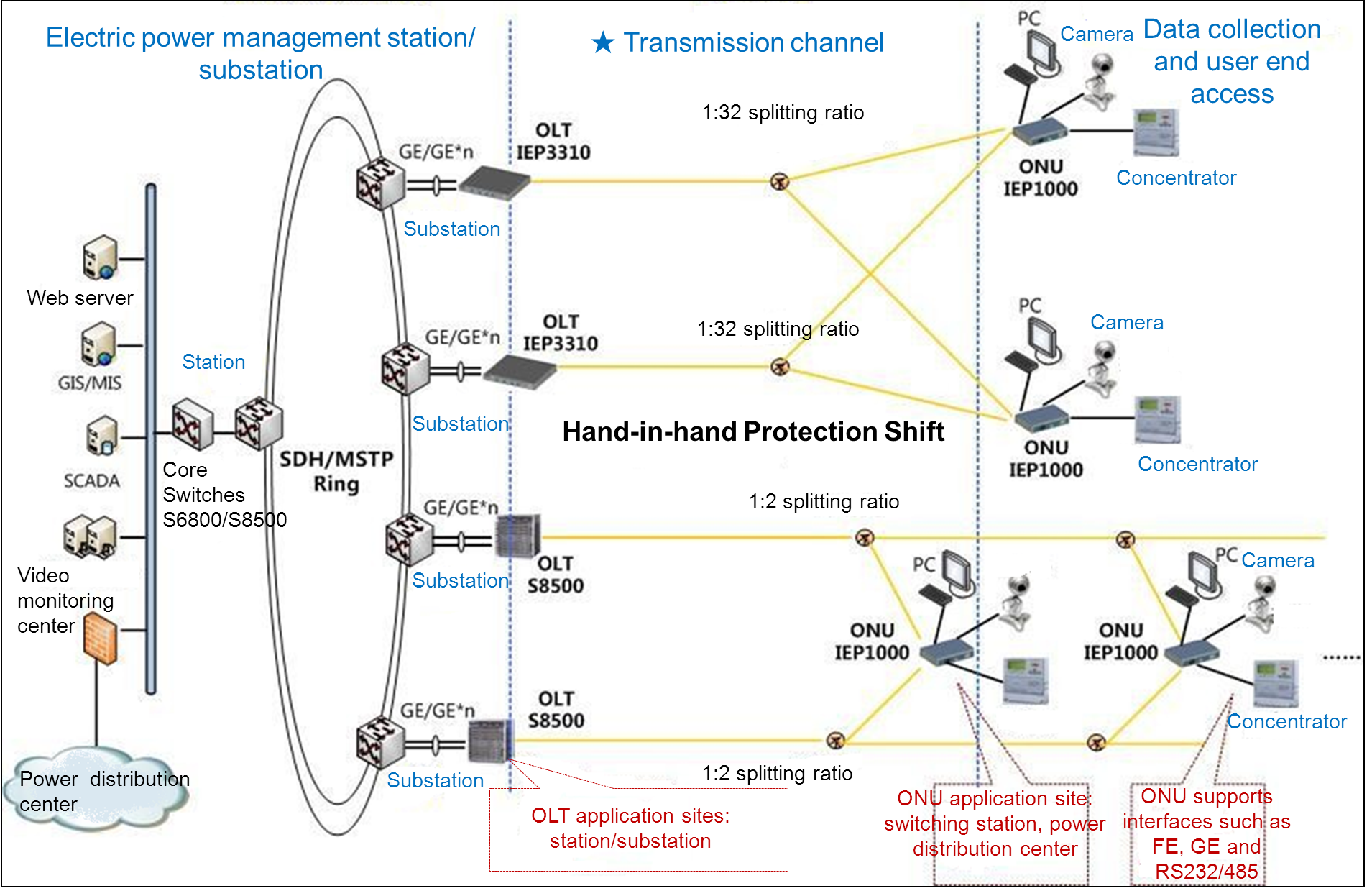
Similar totraditional EPON networking, the EPON system in this solution is also consistedof three parts: OLT, ONU and ODN. The OLTs and ONUs adopted in this solutionare laid out respectively between the 110KV substations and the 10KV switchingstations. Each OLT of the substation are connected to several ONUs throughfibers and passive optical splitters. Each ONU with dual PON interfaces isconnected to two OLTs through fibers. Thus, a topology characterized by Hand-in-handProtection Shift is established.
Each S8500/P3310 OLT and each substation IP/ATMswitch is connected by a single gigabit Ethernet link or multiple gigabitEthernet links. S8500 OLTs and P3310 rack-mounted OLTs can satisfy the need ofsubstations of different scales.
The user network interfaces of ONUs connect to RTUs, TTUs, Networkingmonitoring ends and PCs. BDCOM ONUs support multiple interfaces such as FE, GE,RS232/485, among which RS232/485 interfaces can be flexibly set.
Solution to Electric PowerDistribution Automation Systems (2)
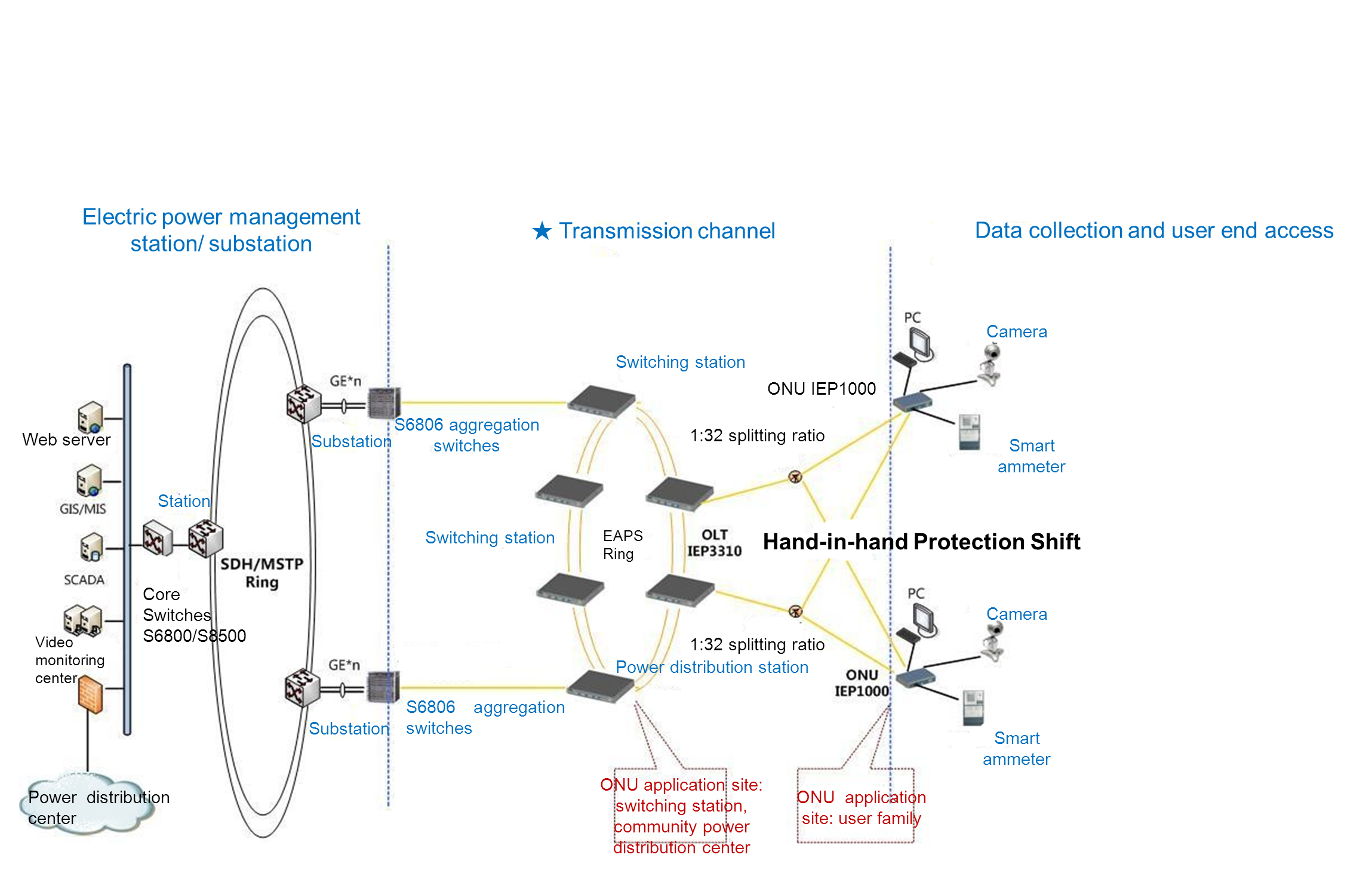
The OLTs and ONUs adopted in this solution are laid out respectivelybetween the 10KV switching stations and the user side. The substations and the10KV switching stations (Ring Main Units) are connected through two fibers. The10KV switching stations constitute a ring network by two fibers, which realizeself-healing with EAPS technology. Each OLT of the switching station isconnected to ONUs in the user side by fibers and passive optical splitters.Each ONU with dual PON interfaces is connected to two OLTs in the 10KVswitching stations through fibers. Thus, a topology characterized by Hand-in-handProtection Shift is established.
The user network interfaces of ONUs connect to RTUs, TTUs, Networkingmonitoring ends and PCs. BDCOM ONUs support multiple interfaces such as FE, GE,RS232/485, among which RS232/485 interfaces can be flexibly set.
Solution to the User Information Collection System
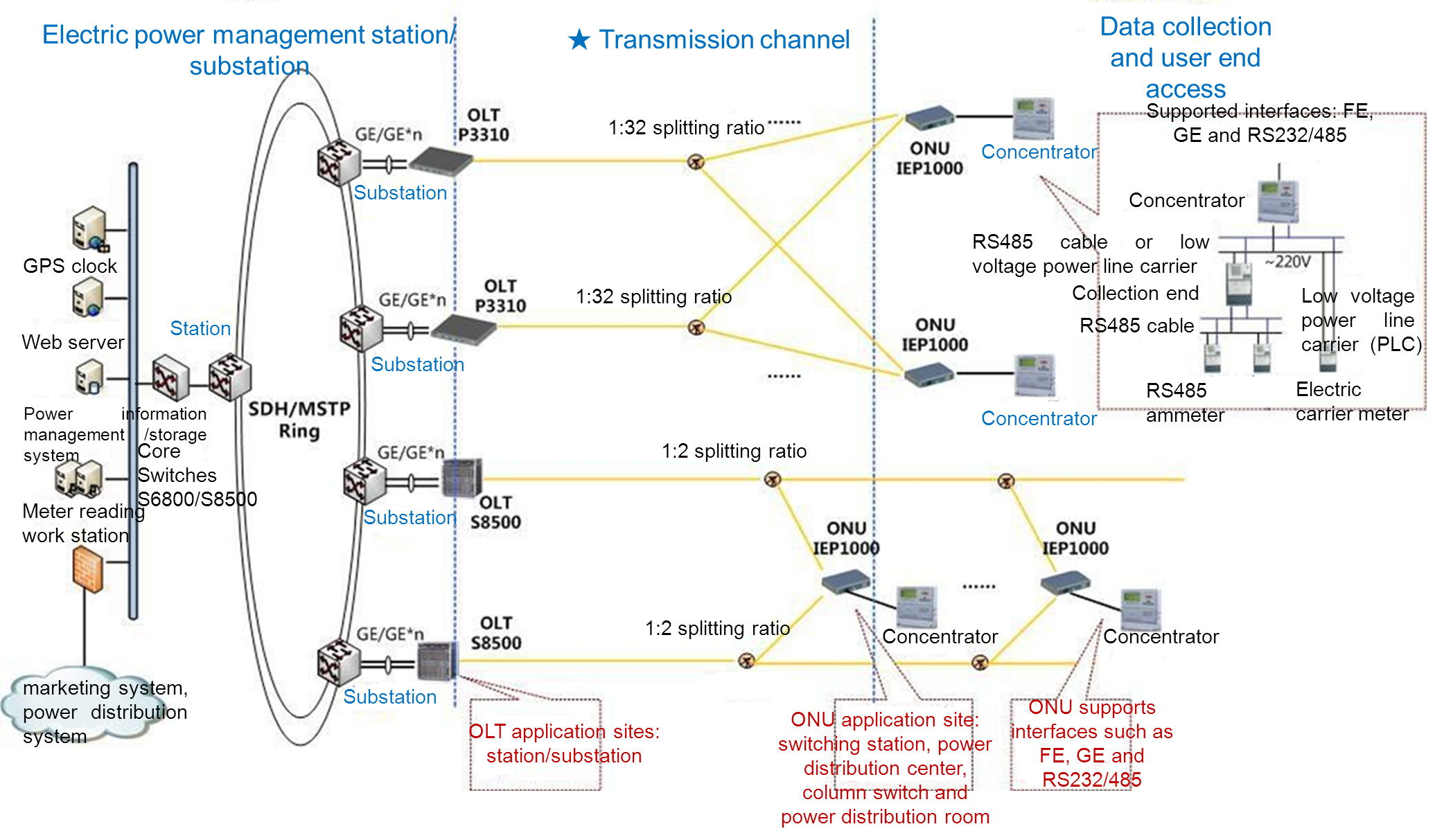
The OLTsand ONUs adopted in this solution are laid out respectively between the 110KVsubstations and the 10KV switching stations. Each OLT of the substation areconnected to several ONUs through fibers and passive optical splitters. EachONU with dual PON interfaces is connected to two OLTs through fibers. Thus, atopology characterized by Hand-in-hand Protection Shift is established.
Each S8500/P3310 OLT and each substation IP/ATM switch is connected by a single gigabitEthernet link or multiple gigabit Ethernet links. S8500 OLTs and P3310rack-mounted OLTs can satisfy the need of substations of different scales.
The user network interfaces of ONUs connect to RTUs, TTUs, Networkingmonitoring ends and PCs. BDCOM ONUs support multiple interfaces such as FE, GE,RS232/485, among which RS232/485 interfaces can be flexibly set.
The data acquisition system in powerdistribution automation is mainly in charge of:
● Dataacquisition (the acquired data include the electric energy data, the AC analogvalue, the work state data, the electric energy over-threshold statistics data,the event record data, etc.);
● Datamanagement (including data reasonability checkup and datacalculating/analyzing/storing);
● Controlfunctions (including control of the rated power, rated electric energy, ratedfee ratio, remoteness, electric fee hand-in aid);
● Comprehensiveapplications (automatic meter's data acquisition control, prepaid fee control,orderly power consumption control, power usage statistics analysis, abnormalpower usage analysis, electric energy quality statistics, line-loss andvalue-added services);
● Operationand maintenance management (system’s time checkup, permission and passwordcontrol, terminal control, file control, communication and routing control,working status control, maintenance and trouble record, report form control);
● Systeminterface (connecting the marketing system, the schedule system and othersystems).